1. GitHub Quickstart#
GitHub is a web-based platform used for version control using Git. It allows multiple people to collaborate on projects, track changes, and manage code. This guide will help you get started with GitHub, covering the basics of creating repositories, committing changes, and collaborating with others.
GitHub welcomes the largest open source communities in the world, with projects like pandas, scikit-learn, PyTorch, TensorFlow and many more. With over 40 millions, GitHub gained such an important position thanks to its amazing collaboration tools and technologies build on top of Git.
1.1. GitHub Quickstart Guide#
1.1.1. Introduction#
This guide will help you get started with GitHub, covering the basics of setting up a GitHub account and cloning the course repository.
1.1.1.1. Prerequisites#
Before you begin, ensure you have the following:
1.1.2. Setting Up Git#
1.1.2.1. Configuring Git#
After installing Git, you need to configure it with your GitHub account. Open your terminal or command prompt and run the following commands:
git config --global user.name "Your Name"
git config --global user.email "your-email@example.com"
1.1.2.2. Cloning a Repository#
Our course is stored on a GitHub repository on remote. In order to have a copy of it on your local machine, you need to clone it from the remote to local.
Open the terminal/command line and navigate to the path where you want to store the course material.
Go to
https://github.com/worldbank/alternative-data-for-crisis, presscodebutton and copy the link for cloning that fits your needs.
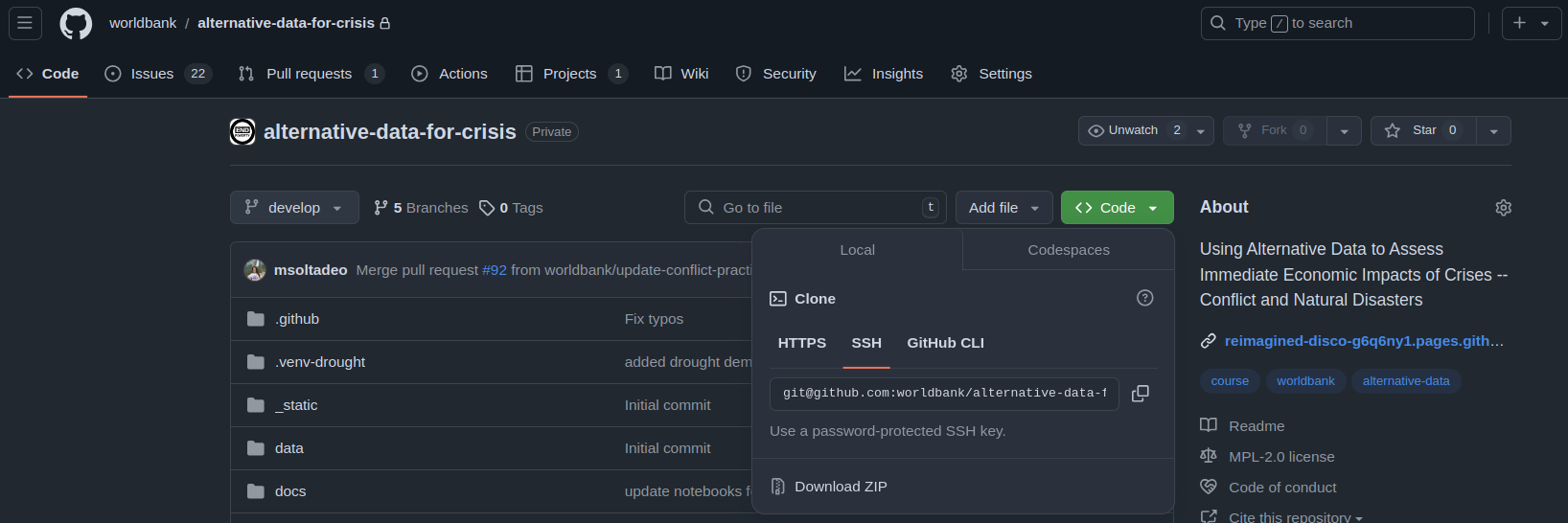
Fig. 1.1 How to obtain the link for cloning a repository#
Go back to the command line, execute the below code and follow the instructions.
git clone "repository-link"
You are all set!
