Using BlackMarblePy#
This Jupyter notebook provides a guided exploration of the BlackMarblePy package, showcasing its capabilities for downloading, visualizing, and analyzing NASA Black Marble nighttime lights data. Through interactive examples, you’ll learn how to:
Download daily, monthly, and yearly data for specific dates, regions, or bounding boxes.
Visualize downloaded data in various forms, including maps and bar charts.
Save visualizations and analysis results for further use.
Requirements#
Before downloading or extracting NASA Black Marble data, make sure the following requirements are met:
📦 Install blackmarblepy#
To use this library, install the BlackMarblePy package. It is highly recommended to install it inside a Python virtual environment to avoid dependency conflicts.
✅ Set Up NASA Earthdata Token#
BlackMarblePy requires a valid, unexpired NASA Earthdata bearer token, which you can retrieve from your Earthdata profile. For ease and security, we recommend setting this as the BLACKMARBLE_TOKEN environment variable on your system.
Access Earthdata Login. In case you haven’t already, you must register.
Select Generate Token. If the token is expired or you are in need of one, click the Generate Token button.
Caution
Please be aware that the “Affiliation” information on your Earthdata profile is mandatory. Without this information, the NASA Earthdata token will be invalid. In case of a download error, try visiting the URL which is failing, as you may be prompted to grant permissions.

Use your token securely. We recommend setting it as a secret or an environment variable rather than hardcoding it. For example, you can set the
BLACKMARBLE_TOKENenvironment variable to store your token safely in Unix-like systems:export BLACKMARBLE_TOKEN=<YOUR_NASA_EARTHDATA_TOKEN>
Important
Using a secret token securely in Python code involves several practices to ensure the token is not exposed unintentionally. For instance, storing the secret token in an environment variable, in configuration files or using secret management services. In this example, we set up an environment variable.
🌍 Define Region of Interest#
You must define a region of interest as a geopandas.GeoDataFrame. This should represent the geographic area you want to extract data for.
For example, we obtain the polygon below from GADM for the state of Ghana.
Fig. 1 This map of Ghana displays the administrative boundaries as obtained from the Global Administrative Areas (GADM) database. The map highlights the regional divisions and key cities, providing a detailed geographic overview of the country. Data source: GADM, version 4.1.#
Examples#
In this section, we will demonstrate how to use BlackMarblePy to download and manipulate NASA Black Marble data.
BlackMarblePy offers two main interfaces:
A class-based interface (
BlackMarble) that retains configuration details like the bearer token and output directory across multiple calls.A procedural API (
bm_extract,bm_raster) that provides the same functionality without requiring an instantiated object, making it convenient for one-off operations.
Both approaches give you flexible options depending on your workflow. We instantiate BlackMarble to use on the examples below.
# Class-based interface example
# Initialize the BlackMarble interface
bm = BlackMarble()
# Optional: configure options
# bm = BlackMarble(
# token="your_token_here", # NASA Earthdata bearer token (can also be set via env var)
# check_all_tiles_exist=True, # Skip dates if any tile is missing
# drop_values_by_quality_flag=[255], # Mask out invalid data (e.g., fill value)
# output_directory="data", # Directory to save outputs
# output_skip_if_exists=True # Skip downloading if file already exists
# )
Create raster of nighttime lights#
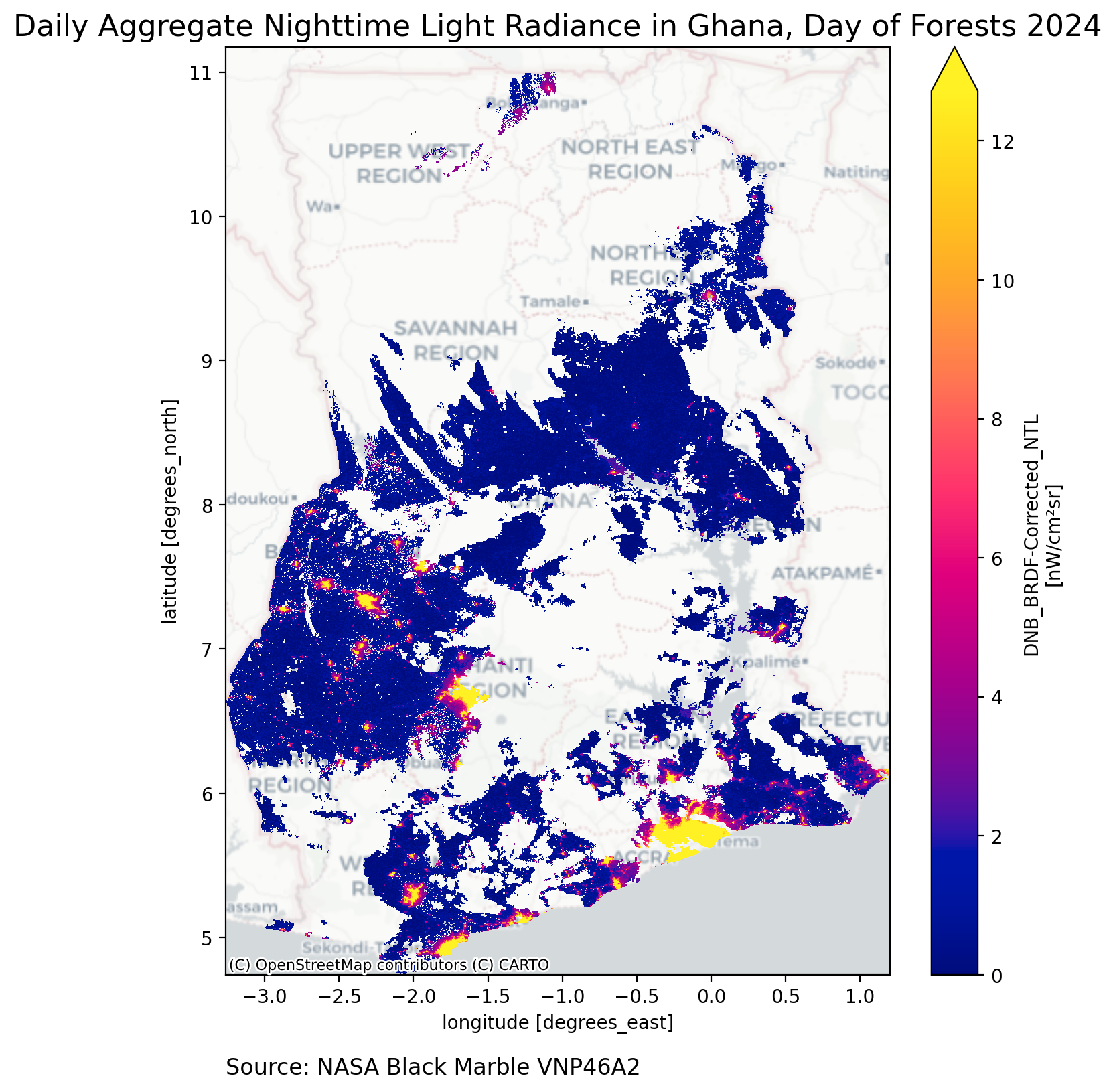
In this section, we show examples of creating daily, monthly, and annual rasters of nighttime lights for the Region of Interest selected. We examine the 2024 International Day of Forests as an example date range.
Daily#
In this section, we retrieve the VNP46A2 product.
VNP46A2 = bm.raster(
gdf,
product_id="VNP46A2",
date_range="2024-03-21",
)
VNP46A2
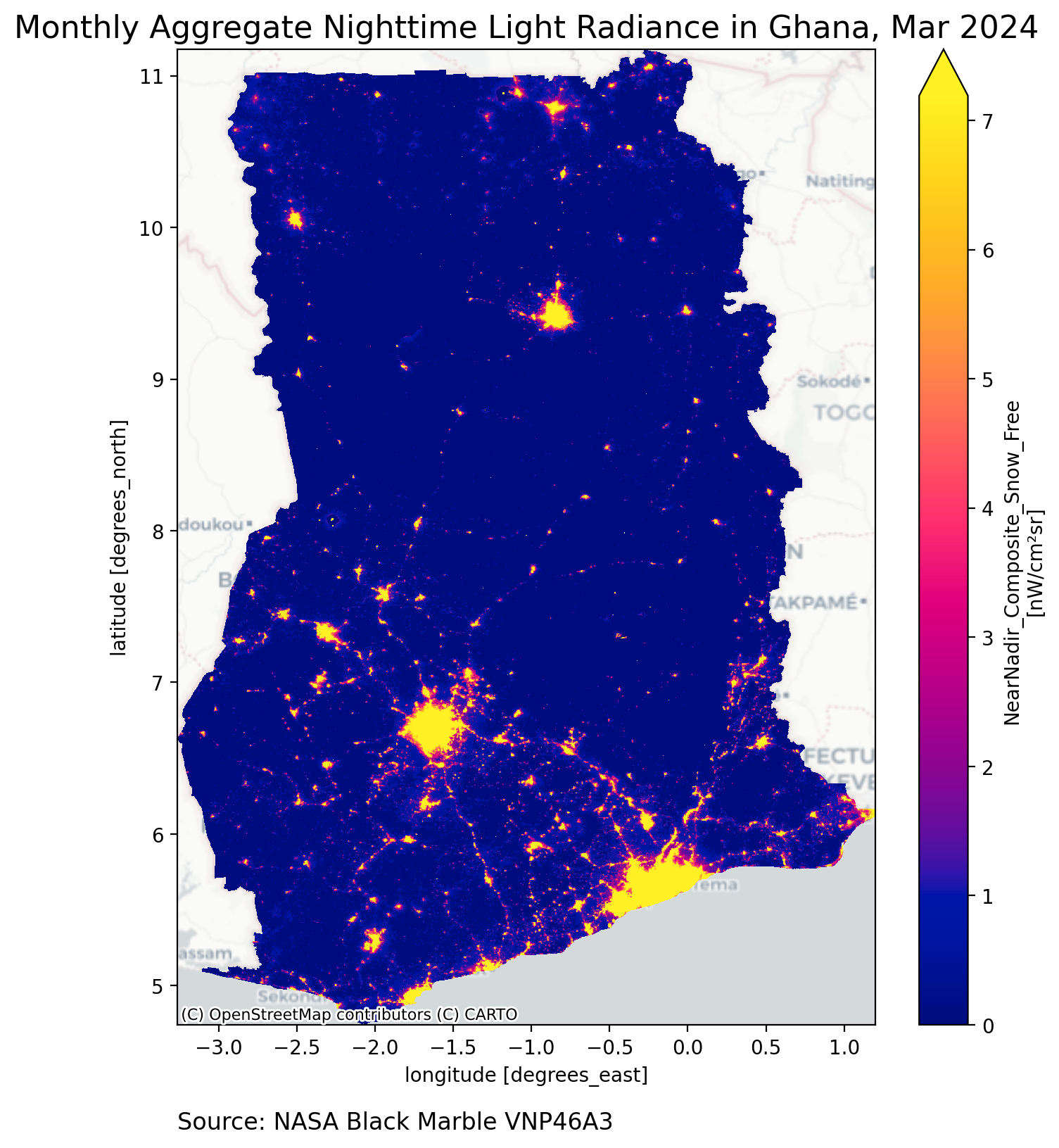
Monthly#
In this section, we retrieve the VNP46A3 product.
VNP46A3 = bm.raster(
gdf,
product_id="VNP46A3",
date_range="2024-03-21",
)
VNP46A3
Annual#
VNP46A4 = bm.raster(
gdf,
product_id="VNP46A4",
date_range="2024-03-21",
)
VNP46A4
Create a raster stack of nighttime lights across multiple time periods#
In this section, we illustrate how to retrieve and extract NASA Black Marble data for multiple time periods. The function will return a raster stack, where each raster band corresponds to a different date. The following code snippet provides examples of getting data across multiple days, months, and years. For each example below, we define a date range using pd.date_range.
Daily#
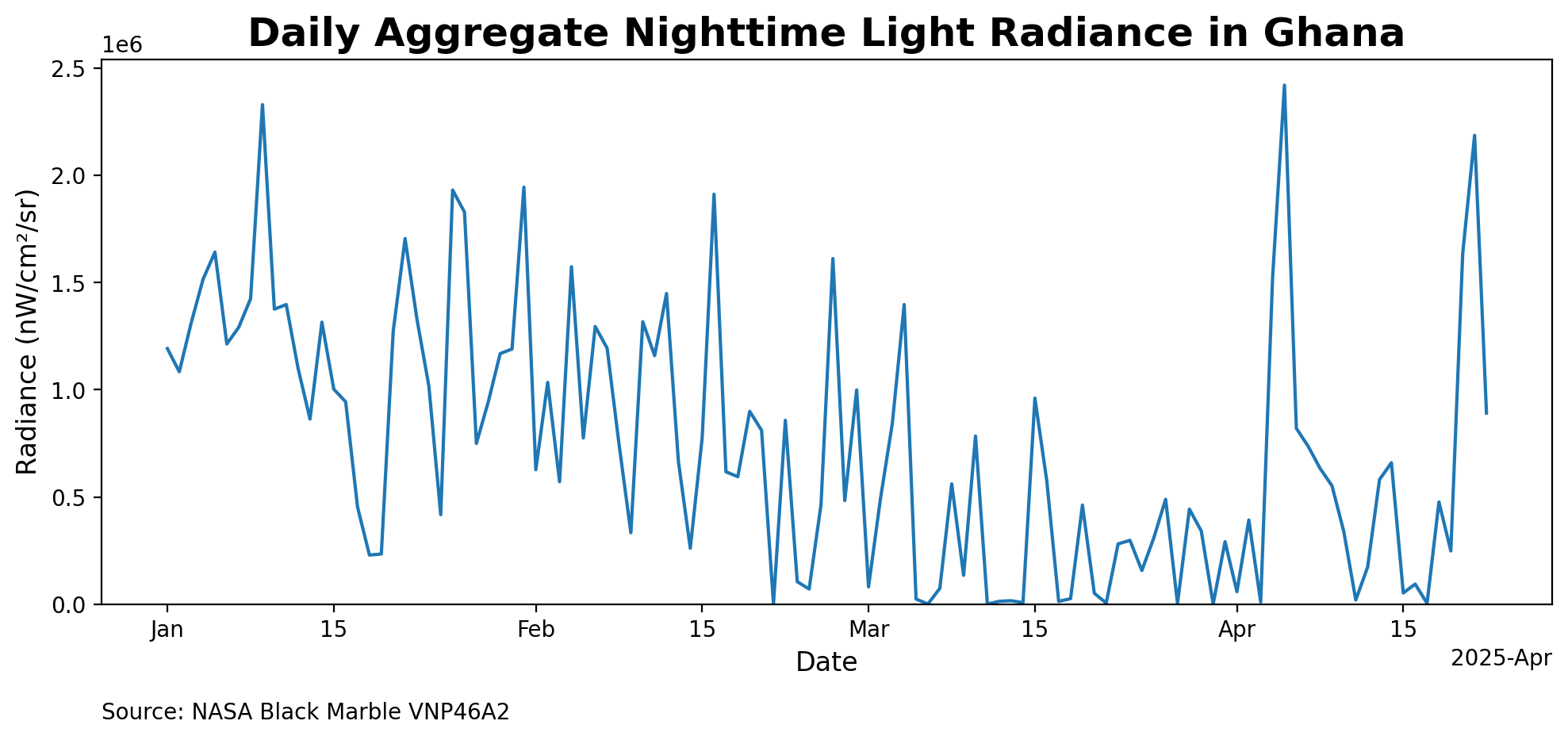
To celebrate Earth Day and to exemplify the daily VNP46A2 product, we examine a period leading to April 22, 2025 in this example.
# Raster stack of daily data
r_daily = bm.raster(
gdf,
product_id="VNP46A2",
date_range=pd.date_range("2025-01-01", "2025-04-22", freq="D"),
)
<xarray.Dataset> Size: 1GB
Dimensions: (x: 1071, y: 1544, time: 112)
Coordinates:
* x (x) float64 9kB -3.26 -3.256 -3.252 ... 1.194 1.198
* y (y) float64 12kB 11.17 11.17 11.16 ... 4.748 4.744
* time (time) datetime64[ns] 896B 2025-01-01 ... 2025-04-22
Data variables:
DNB_BRDF-Corrected_NTL (time, y, x) float64 1GB nan nan nan ... nan nan nan
Attributes: (12/42)
AlgorithmType: b'SCI'
AlgorithmVersion: b'NPP_PR46A2 1.0.3'
comment: b'For additional information regarding...
Conventions: b'CF-1.6'
creator_email: b'modis-ops@lists.nasa.gov'
creator_name: b'VIIRS Land SIPS Processing Group'
... ...
VerticalTileNumber: b'08'
WestBoundingCoord: 0.0
AREA_OR_POINT: Area
scale_factor: 1.0
add_offset: 0.0
_FillValue: nan
Fig. 2 This figures describes the daily average nighttime lights radiance data plotted over time. The data reflects fluctuations in radiance levels due to varying cloud cover, affecting the accuracy of the measurements#
Monthly#
In this section, we examine an example for the monthly VNP46A3 product.
# Raster stack of monthly data
r_monthly = bm.raster(
gdf,
product_id="VNP46A3",
date_range=pd.date_range("2023-01-01", "2025-04-01", freq="MS"),
)
<xarray.Dataset> Size: 370MB
Dimensions: (x: 1071, y: 1544, time: 28)
Coordinates:
* x (x) float64 9kB -3.26 -3.256 ... 1.194 1.198
* y (y) float64 12kB 11.17 11.17 ... 4.748 4.744
* time (time) datetime64[ns] 224B 2023-01-01 ... ...
Data variables:
NearNadir_Composite_Snow_Free (time, y, x) float64 370MB nan nan ... nan
Attributes: (12/42)
AlgorithmType: b'SCI'
AlgorithmVersion: b'NPP_PR46A3 2.0.0'
Conventions: b'CF-1.6'
creator_email: b'modis-ops@lists.nasa.gov'
creator_name: b'VIIRS Land SIPS Processing Group'
creator_url: b'https://ladsweb.modaps.eosdis.nasa.gov'
... ...
VerticalTileNumber: b'07'
WestBoundingCoord: 0.0
AREA_OR_POINT: Area
scale_factor: 1.0
add_offset: 0.0
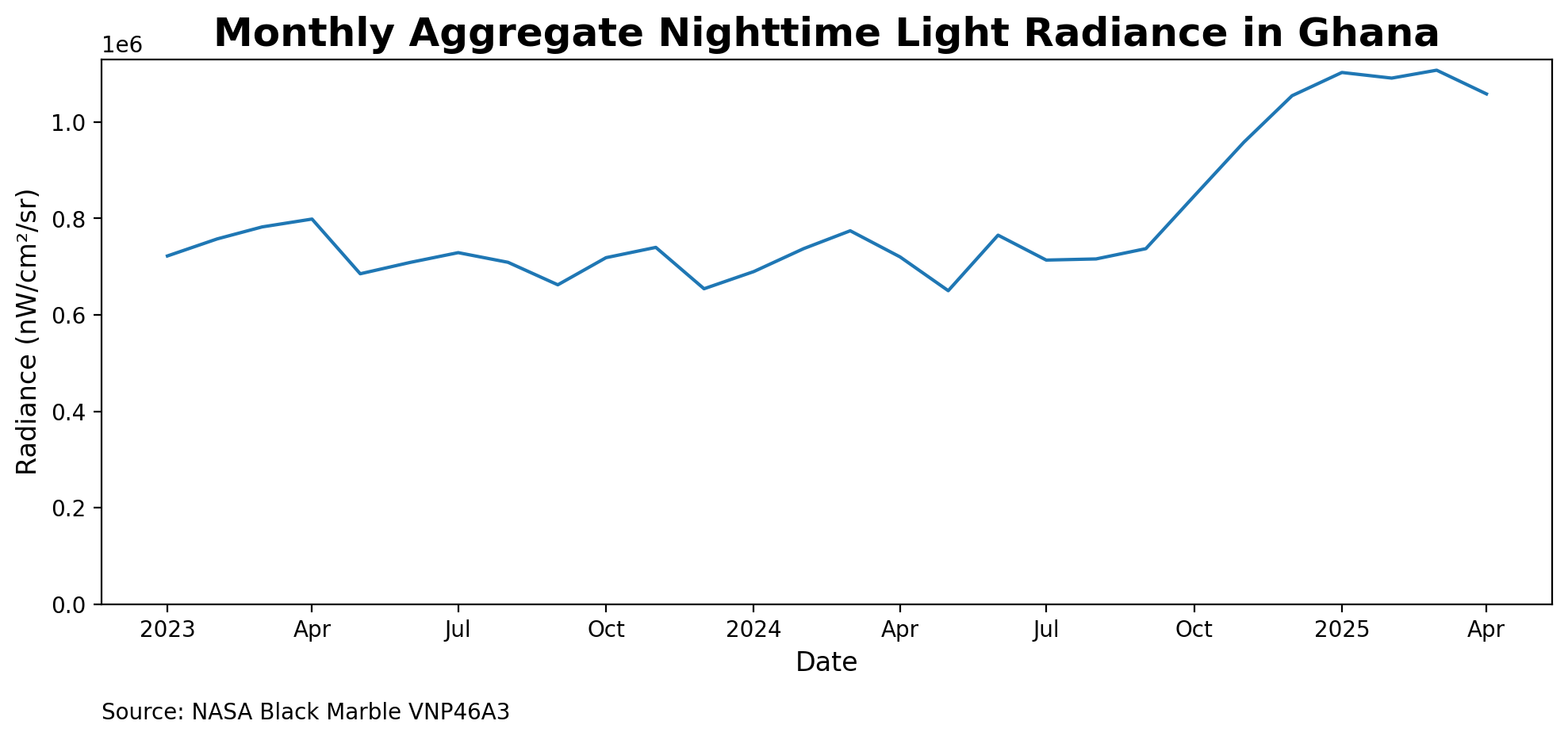
_FillValue: nanFig. 3 This figures describes the monthly average nighttime lights radiance data plotted over time. The data reflects fluctuations in radiance levels due to varying cloud cover, affecting the accuracy of the measurements#
Yearly#
In this section, we examine an example for the yearly VNP46A4 product.
# Raster stack of yearly data
r_yearly = bm.raster(
gdf,
product_id="VNP46A4",
date_range=pd.date_range("2019-01-01", "2024-01-01", freq="YS"),
)
<xarray.Dataset> Size: 79MB
Dimensions: (x: 1071, y: 1544, time: 6)
Coordinates:
* x (x) float64 9kB -3.26 -3.256 ... 1.194 1.198
* y (y) float64 12kB 11.17 11.17 ... 4.748 4.744
* time (time) datetime64[ns] 48B 2019-01-01 ... 2...
Data variables:
NearNadir_Composite_Snow_Free (time, y, x) float64 79MB nan nan ... nan nan
Attributes: (12/42)
AlgorithmType: b'SCI'
AlgorithmVersion: b'NPP_PR46A3 2.0.0'
Conventions: b'CF-1.6'
creator_email: b'modis-ops@lists.nasa.gov'
creator_name: b'VIIRS Land SIPS Processing Group'
creator_url: b'https://ladsweb.modaps.eosdis.nasa.gov'
... ...
VerticalTileNumber: b'07'
WestBoundingCoord: -10.0
AREA_OR_POINT: Area
scale_factor: 1.0
add_offset: 0.0
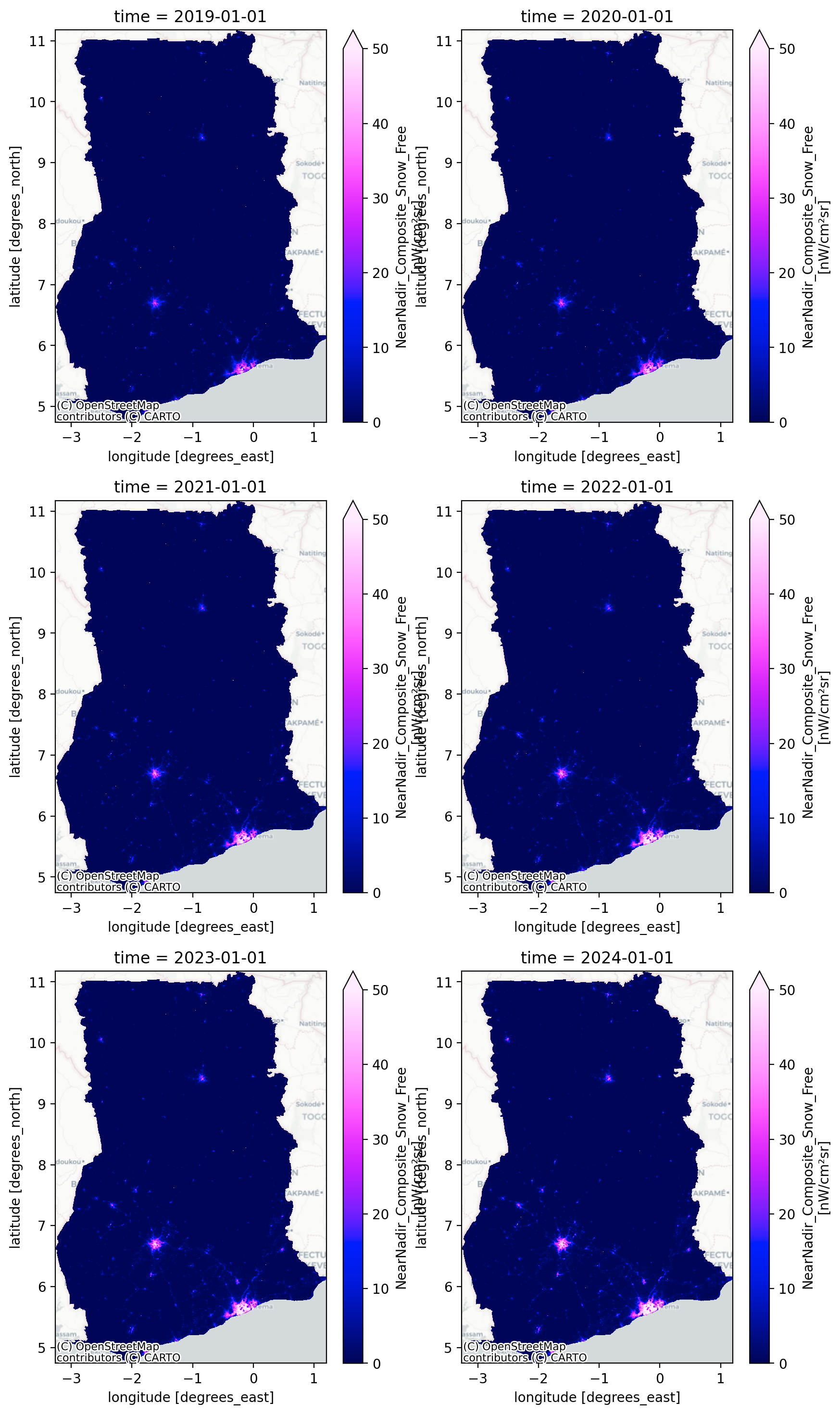
_FillValue: nanFig. 4 Temporal variation of NearNadir_Composite_Snow_Free mapped over multiple years. Each subplot represents a different time period overlaid with a basemap.#
Visualizing difference in radiance year over year#
Lastly, we are now able to compare and calculate the increase/decrease in nighttime lights radiance levels across different points in time.
Fig. 5 This figure displays the percentage change in radiance for Ghana between 2019 and 2022. The data, sourced from NASA’s Black Marble VNP46A3 product is visualized with basemap.#
Compute nighttime lights zonal statistics over time#
In this section, we use the bm_extract function to observe treends in nighttime lights over time. The bm_extract function leverages the rasterstats package to aggregate nighttime lights data to polygons. In the following example, we show trends in annual nighttime lights data across Ghana’s first-administrative divisions.
VNP46A4 = bm.extract(
gdf,
"VNP46A4",
pd.date_range("2012-01-01", "2024-01-01", freq="YS"),
)
Fig. 6 This figure illustrates the trend in nighttime lights radiance across Ghana over the period from 2012 to 2023. The X-axis represents the years from 2012 to 2024, while the Y-axis measures the radiance in nanowatts per square centimeter per steradian (nW/cm²/sr). The data highlights changes in light intensity, which can be indicative of economic activity, urbanization, and infrastructure development. Data source: NASA Black Marble VNP46A4 retrieved with BlackMarblePy.#
Downloading and Storing Black Marble data#
In this section, we provide a guide on using BlackMarblePy to download NASA Black Marble data and save it to a specified local directory. You can use the output_directory parameter to designate the directory for saving the files. By default, files that have already been downloaded will not be re-downloaded in subsequent executions.
BlackMarble(
output_directory="data/", # Save files to local data/ directory
output_skip_if_exists=True, # Set to skip if exists
).raster(
gdf,
product_id,
date_range,
)
Alternatively, set output_skip_if_exists=False to force the redownload of files from NASA.
References#
- 1
Miguel O. Román, Zhuosen Wang, Qingsong Sun, Virginia Kalb, Steven D. Miller, Andrew Molthan, Lori Schultz, Jordan Bell, Eleanor C. Stokes, Bhartendu Pandey, Karen C. Seto, Dorothy Hall, Tomohiro Oda, Robert E. Wolfe, Gary Lin, Navid Golpayegani, Sadashiva Devadiga, Carol Davidson, Sudipta Sarkar, Cid Praderas, Jeffrey Schmaltz, Ryan Boller, Joshua Stevens, Olga M. Ramos González, Elizabeth Padilla, José Alonso, Yasmín Detrés, Roy Armstrong, Ismael Miranda, Yasmín Conte, Nitza Marrero, Kytt MacManus, Thomas Esch, and Edward J. Masuoka. Nasa's black marble nighttime lights product suite. Remote Sensing of Environment, 210:113–143, 2018. URL: https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S003442571830110X, doi:https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rse.2018.03.017.
- 2
Gabriel Stefanini Vicente and Robert Marty. BlackMarblePy: Georeferenced Rasters and Statistics of Nighttime Lights from NASA Black Marble. https://worldbank.github.io/blackmarblepy, 2023. URL: https://worldbank.github.io/blackmarblepy, doi:10.5281/zenodo.10667907.