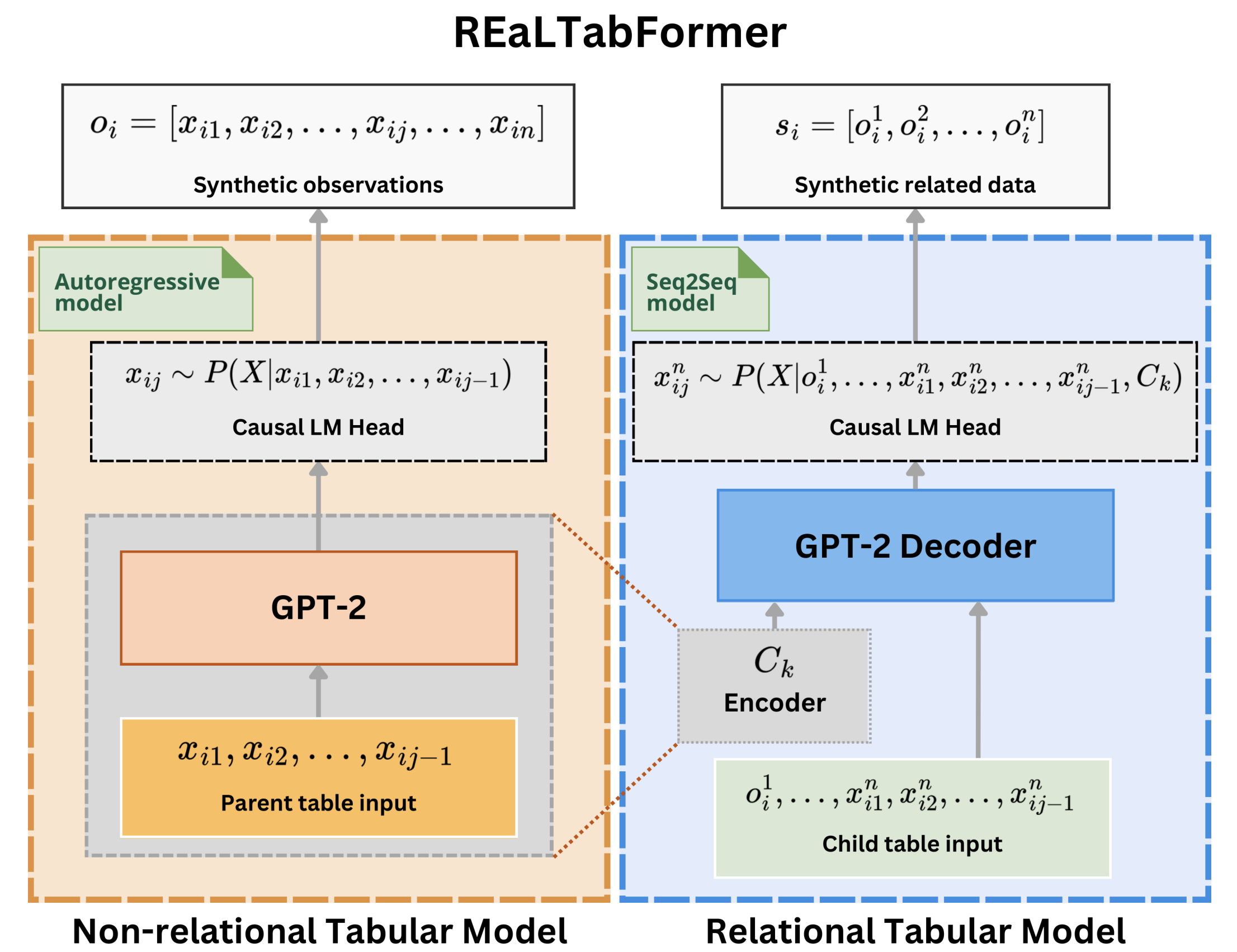
import logging
import random
import re
import time
import uuid
import warnings
from dataclasses import dataclass, fields
from typing import Dict, List, Optional, Tuple
import numpy as np
import pandas as pd
from datasets import Dataset
[docs]TEACHER_FORCING_PRE = "_TEACHERFORCING"
[docs]INVALID_NUMS_RE = r"[^\-.0-9]"
@dataclass(frozen=True)
[docs]class TabularArtefact:
[docs] best_disc_model: str = "best-disc-model"
[docs] mean_best_disc_model: str = "mean-best-disc-model"
[docs] not_best_disc_model: str = "not-best-disc-model"
[docs] last_epoch_model: str = "last-epoch-model"
@staticmethod
[docs] def artefacts():
return [field.default for field in fields(TabularArtefact)]
@dataclass(frozen=True)
[docs]class ModelFileName:
[docs] rtf_config_json: str = "rtf_config.json"
[docs] rtf_model_pt: str = "rtf_model.pt"
@staticmethod
[docs] def names():
return [field.default for field in fields(ModelFileName)]
@dataclass(frozen=True)
[docs]class ModelType:
[docs] tabular: str = "tabular"
[docs] relational: str = "relational"
@staticmethod
[docs] def types():
return [field.default for field in fields(ModelType)]
@dataclass(frozen=True)
[docs]class ColDataType:
[docs] NUMERIC: str = "NUMERIC"
[docs] DATETIME: str = "DATETIME"
[docs] CATEGORICAL: str = "CATEGORICAL"
@staticmethod
[docs] def types():
return [field.default for field in fields(ColDataType)]
@dataclass(frozen=True)
[docs]class SpecialTokens:
[docs] SPTYPE: str = "[SPTYPE]"
@staticmethod
[docs] def tokens():
return [field.default for field in fields(SpecialTokens)]
[docs]def get_uuid():
return uuid.uuid4().hex
[docs]def fix_multi_decimal(v):
if v.count(".") > 1:
v = v.split(".")
v = ".".join([v[0], "".join(v[1:])])
return v
[docs]def build_vocab(df: pd.DataFrame = None, special_tokens=None, add_columns: bool = True):
assert (
df is not None
) or special_tokens, "At least one of `df` or `special_tokens` must not be None."
if add_columns and df is not None:
# We limit this feature to data that are likely
# to have been processed using the convention imposed
# where we keep track of the column index in the processed data.
assert df.columns.str[0].str.isdigit().all()
id2token = {}
curr_id = 0
if special_tokens:
id2token.update(dict(enumerate(special_tokens)))
curr_id = max(id2token) + 1
column_token_ids = {}
if df is not None:
for col in df.columns:
id2token.update(dict(enumerate(sorted(df[col].unique()), curr_id)))
column_token_ids[col] = list(range(curr_id, max(id2token) + 1))
curr_id = max(id2token) + 1
if add_columns:
id2token.update(
dict(
enumerate(
[extract_processed_column(col) for col in df.columns], curr_id
)
)
)
# Add this here to prevent a semantic error in case we add another
# set of tokens later.
curr_id = max(id2token) + 1
token2id = {v: k for k, v in id2token.items()}
return dict(
id2token=id2token,
token2id=token2id,
column_token_ids=column_token_ids,
)
[docs]def process_numeric_data(
series: pd.Series,
max_len: int = 10,
numeric_precision: int = 4,
transform_data: Dict = None,
) -> Tuple[pd.Series, Dict]:
is_transform = True
if transform_data is None:
transform_data = dict()
is_transform = False
if is_transform:
warnings.warn(
"Default values will be overridden because transform_data was passed..."
)
max_len = transform_data["max_len"]
numeric_precision = transform_data["numeric_precision"]
else:
transform_data["max_len"] = max_len
transform_data["numeric_precision"] = numeric_precision
# Note that at this point, we should have casted int-like values to
# pd.Int64Dtype but just to be very sure, let's do that again here.
try:
series = series.astype(pd.Int64Dtype())
except TypeError:
pass
except ValueError:
pass
if series.dtype == pd.Int64Dtype():
series = series.astype(str)
else:
# We convert float-like values to string with the specified
# maximum precision.
# NOTE: Don't use series.round(numeric_precision).astype(str)
# In some cases, this introduces scientific notation in the
# string version causing "invalid" values.
# Note that our purpose for doing this is to actually truncate
# the precision and not increase the precision.
# So, we strip the right trailing zeros because the formatting
# pads the series to the numeric_precision even when not needed.
series = series.map(lambda x: f"{x:.{numeric_precision}f}").str.rstrip("0")
# Get the most significant digit
if is_transform:
mx_sig = transform_data["mx_sig"]
else:
mx_sig = series.str.find(".").max()
transform_data["mx_sig"] = int(mx_sig)
if mx_sig <= 0:
# The data has no decimal point.
# Pad the data with leading zeros if not
# aligned to the largest value.
# We also don't apply the max_len to integral
# valued data because it will basically
# remove important information.
if is_transform:
zfill = transform_data["zfill"]
else:
zfill = series.map(len).max()
transform_data["zfill"] = int(zfill)
series = series.str.zfill(zfill)
else:
# Make sure that we don't exessively truncate the data.
# The max_len should be greater than the mx_sig.
# Add a +1 to generate a minimum of tenth place resolution
# for this data.
assert max_len > (
mx_sig + 1
), f"The target length {max_len} of the data doesn't include the numeric precision at {mx_sig}. Increase max_len to at least {max_len + (mx_sig + 2 - max_len)}."
# Left align first based on the magnitude of the values.
# We compute the difference in the most significant digits
# of all values with respect to the largest value.
# We then pad a leading zero to values with lower most significant
# digits.
# For example we have the values 1029.61 and 4.269. This will
# determine that 1029.61 has the largest magnitude, with most significant
# digit of 4. It will pad the value 4.269 with three zeros and convert it
# to 0004.269.
series = (mx_sig - series.str.find(".")).map(lambda x: "0" * x) + series
series = series.str[:max_len]
# We additionally apply left justify to align based on the trailing precision.
# For example, we have 1029.61 and 0004.269 as values. This time we transform the first
# value to become 1029.610 to align with the precision of the second value.
if is_transform:
ljust = transform_data["ljust"]
else:
ljust = series.map(len).max()
transform_data["ljust"] = int(ljust)
series = series.str.ljust(ljust, "0")
# If a number has a negative sign, make sure that it is placed properly.
series.loc[series.str.contains("-", regex=False)] = "-" + series.loc[
series.str.contains("-", regex=False)
].str.replace("-", "", regex=False)
return series, transform_data
[docs]def process_datetime_data(
series, transform_data: Dict = None
) -> Tuple[pd.Series, Dict]:
# Get the max_len from the current time.
# This will be ignored later if the actual max_len
# is shorter.
max_len = len(str(int(time.time())))
# Convert the datetimes to
# their equivalent timestamp values.
# Make sure that we don't convert the NaT
# to some integer.
series = series.copy()
# Track null values (NaT)
null_idx = series.isnull()
# Convert to the numerical representation
# of the datetime (UNIX timestamp)
series = (series.astype("int64") / 1e9)
# Fill NA
series.loc[null_idx] = pd.NA
# Cast as integer type
series = series.astype("Int64")
# Take the mean value to re-align the data.
# This will help reduce the scale of the numeric
# data that will need to be generated. Let's just
# add this offset back later before casting.
mean_date = None
if transform_data is None:
mean_date = int(series.mean())
series -= mean_date
else:
# The mean_date should have been
# stored during fitting.
series -= transform_data["mean_date"]
# Then apply the numeric data processing
# pipeline.
series, transform_data = process_numeric_data(
series,
max_len=max_len,
numeric_precision=0,
transform_data=transform_data,
)
# Store the `mean_date` here because `process_numeric_data`
# expects a None transform_data during fitting.
if mean_date is not None:
transform_data["mean_date"] = mean_date
return series, transform_data
[docs]def process_categorical_data(series: pd.Series) -> pd.Series:
# Simply convert the categorical data to string.
return series.astype(str)
[docs]def encode_partition_numeric_col(col, tr, col_zfill):
# Generate a derived column name for the partitioned
# numeric data. For example: Latitude_00, Latitude_01, etc.
return [f"{col}_{str(i).zfill(col_zfill)}" for i in range(len(tr.columns))]
[docs]def decode_partition_numeric_col(partition_col):
# Decode the encoded column for the partitioned numeric data.
# For example: Latitude_00 -> Latitude, Latitude_01 -> Latitude, etc.
return "_".join(partition_col.split("_")[:-1])
[docs]def tokenize_numeric_col(series: pd.Series, nparts=2, col_zfill=2):
# After normalizing the numeric values, we then segment
# them based on a fixed partition size (nparts).
col = series.name
max_len = series.map(len).min()
# Take the observations that have non-numeric characters.
# These are NaNs.
nan_obs = series.str.contains(INVALID_NUMS_RE, regex=True)
if nparts > max_len > 2:
# Allow minimum of 0-99 as acceptable singleton range.
raise ValueError(
f"Partition size {nparts} is greater than the value length {max_len}. Consider reducing the number of partitions..."
)
mx = series.map(len).max()
tr = pd.concat([series.str[i : i + nparts] for i in range(0, mx, nparts)], axis=1)
# Replace values with NUMERIC_NA_TOKEN
tr.loc[nan_obs] = NUMERIC_NA_TOKEN * nparts
tr.columns = encode_partition_numeric_col(col, tr, col_zfill)
return tr
[docs]def encode_column_values(series):
return series.name + SPECIAL_COL_SEP + series
[docs]def decode_column_values(series):
# return series.str.split(SPECIAL_COL_SEP).map(lambda x: x[-1])
return series.map(lambda x: x.split(SPECIAL_COL_SEP)[-1])
[docs]def encode_processed_column(idx, dtype, col):
# The idx indicates the position of the column in the original
# data.
# The dtype corresponds to the data type of the column.
# The col is the actual column name of the data in the table.
assert dtype in ColDataType.types()
return f"{idx}{SPECIAL_COL_SEP}{dtype}{SPECIAL_COL_SEP}{col}"
[docs]def decode_processed_column(col):
# Reverts the process in `encode_processed_column`
# Do nothing if the format is not as expected.
if not any([dtype in col for dtype in ColDataType.types()]):
return col
# Pattern is: [0-9]+___(NUMERIC|DATETIME|CATEGORICAL)___
return re.sub(
f"[0-9]+{SPECIAL_COL_SEP}({'|'.join(ColDataType.types())}){SPECIAL_COL_SEP}",
"",
col,
)
[docs]def extract_processed_column(col):
# Extracts the data generated by `encode_processed_column`
# Return None if not found.
# Pattern is: ([0-9]+___(NUMERIC|DATETIME|CATEGORICAL)___.*)?____
match = re.match(
f"[0-9]+{SPECIAL_COL_SEP}({'|'.join(ColDataType.types())})",
col,
)
return match.group(0) if match else None
[docs]def is_numeric_col(col):
return f"{SPECIAL_COL_SEP}{ColDataType.NUMERIC}{SPECIAL_COL_SEP}" in col
[docs]def is_datetime_col(col):
return f"{SPECIAL_COL_SEP}{ColDataType.DATETIME}{SPECIAL_COL_SEP}" in col
[docs]def is_categorical_col(col):
return f"{SPECIAL_COL_SEP}{ColDataType.CATEGORICAL}{SPECIAL_COL_SEP}" in col
[docs]def is_numeric_datetime_col(col):
return is_numeric_col(col) or is_datetime_col(col)
[docs]def process_data(
df: pd.DataFrame,
numeric_max_len=10,
numeric_precision=4,
numeric_nparts=2,
first_col_type=None,
col_transform_data: Dict = None,
target_col: str = None,
) -> Tuple[pd.DataFrame, Dict]:
# This should receive a dataframe with dtypes that have already been
# properly categorized between numeric and categorical.
# Date type can be converted as UNIX timestamps.
assert first_col_type in [None, ColDataType.CATEGORICAL, ColDataType.NUMERIC]
df = df.copy()
# Unify the variable for missing data
df = df.fillna(pd.NA)
# Force cast integral values to Int64Dtype dtype
# to save precision if they are represented as float.
for c in df:
try:
if pd.api.types.is_datetime64_any_dtype(df[c].dtype):
# Don't cast datetime types.
continue
if pd.api.types.is_numeric_dtype(df[c].dtype):
# Only cast if the column is explicitly numeric type.
df[c] = df[c].astype(pd.Int64Dtype())
except TypeError:
pass
except ValueError:
pass
if target_col is not None:
assert (
first_col_type is None
), "Implicit ordering of columns when teacher-forcing of target is used is not supported yet!"
tf_col_name = f"{TEACHER_FORCING_PRE}_{target_col}"
assert (
tf_col_name not in df.columns
), f"The column name ({tf_col_name}) must not be in the raw data. Found instead..."
target_ser = df[target_col].copy()
target_ser.name = tf_col_name
df = pd.concat([target_ser, df], axis=1)
# Rename the columns to encode the original order by adding a suffix of increasing
# integer values.
num_cols = len(str(len(df.columns)))
col_idx = {col: f"{str(i).zfill(num_cols)}" for i, col in enumerate(df.columns)}
# Create a dataframe that will hold the processed data
processed_series = []
# Process numerical data
numeric_cols = df.select_dtypes(include=np.number).columns
if col_transform_data is None:
col_transform_data = dict()
for c in numeric_cols:
col_name = encode_processed_column(col_idx[c], ColDataType.NUMERIC, c)
_col_transform_data = col_transform_data.get(c)
series, transform_data = process_numeric_data(
df[c],
max_len=numeric_max_len,
numeric_precision=numeric_precision,
transform_data=_col_transform_data,
)
if _col_transform_data is None:
# This means that no transform data is available
# before the processing.
col_transform_data[c] = transform_data
series.name = col_name
processed_series.append(series)
# Process datetime data
datetime_cols = df.select_dtypes(include="datetime").columns
for c in datetime_cols:
col_name = encode_processed_column(col_idx[c], ColDataType.DATETIME, c)
_col_transform_data = col_transform_data.get(c)
series, transform_data = process_datetime_data(
df[c],
transform_data=_col_transform_data,
)
if _col_transform_data is None:
# This means that no transform data is available
# before the processing.
col_transform_data[c] = transform_data
series.name = col_name
processed_series.append(series)
processed_df = pd.concat([pd.DataFrame()] + processed_series, axis=1)
if not processed_df.empty:
# Combine the processed numeric and datetime data.
processed_df = pd.concat(
[
tokenize_numeric_col(processed_df[col], nparts=numeric_nparts)
for col in processed_df.columns
],
axis=1,
)
# NOTE: The categorical data should be the last to be processed!
categorical_cols = df.columns.difference(numeric_cols).difference(datetime_cols)
if not categorical_cols.empty:
# Process the rest of the data, assumed to be categorical values.
processed_df = pd.concat(
[
processed_df,
*(
process_categorical_data(df[c]).rename(
encode_processed_column(col_idx[c], ColDataType.CATEGORICAL, c)
)
for c in categorical_cols
),
],
axis=1,
)
# Get the different sets of column types
cat_cols = processed_df.columns[
processed_df.columns.str.contains(ColDataType.CATEGORICAL)
]
numeric_cols = processed_df.columns[
~processed_df.columns.str.contains(ColDataType.CATEGORICAL)
]
if first_col_type == ColDataType.CATEGORICAL:
df = processed_df[cat_cols.union(numeric_cols, sort=False)]
elif first_col_type == ColDataType.NUMERIC:
df = processed_df[numeric_cols.union(cat_cols, sort=False)]
else:
# Reorder columns to the original order
df = processed_df[sorted(processed_df.columns)]
for c in df.columns:
# Add the column name as part of the value.
df[c] = encode_column_values(df[c])
return df, col_transform_data
[docs]def get_token_id(
token: str, vocab_token2id: Dict[str, int], mask_rate: float = 0
) -> int:
token_id = vocab_token2id.get(token, vocab_token2id[SpecialTokens.UNK])
if mask_rate > 0:
token_id = (
vocab_token2id[SpecialTokens.RMASK]
if random.random() < mask_rate
else token_id
)
return token_id
[docs]def make_dataset(
df: pd.DataFrame,
vocab: Dict,
mask_rate: float = 0,
affix_eos: bool = True,
return_token_type_ids: bool = False,
) -> Dataset:
# Load the dataframe into a HuggingFace Dataset
training_dataset = Dataset.from_pandas(df, preserve_index=False)
# Create the input_ids and label_ids columns
logging.info("Creating the input_ids and label_ids columns...")
return training_dataset.map(
lambda example: get_input_ids(
example,
vocab,
df.columns,
mask_rate=mask_rate,
affix_eos=affix_eos,
return_token_type_ids=return_token_type_ids,
),
remove_columns=training_dataset.column_names,
)
[docs]def make_relational_dataset(
in_df: pd.DataFrame,
out_df: pd.DataFrame,
vocab: dict,
in_out_idx: dict,
mask_rate=0,
output_max_length: Optional[int] = None,
return_token_type_ids: bool = False,
) -> Dataset:
# Relational data
# Load the dataframe into a HuggingFace Dataset
encoder_dataset = Dataset.from_pandas(in_df, preserve_index=False)
# Load the dataframe into a HuggingFace Dataset
decoder_dataset = Dataset.from_pandas(out_df, preserve_index=False)
# Do not add [BOS] and [EOS] here. This will be handled
# in the creation of the training_dataset in `get_relational_input_ids`.
decoder_dataset = decoder_dataset.map(
lambda example: get_input_ids(
example,
vocab["decoder"],
out_df.columns,
mask_rate=mask_rate,
return_label_ids=False,
return_token_type_ids=return_token_type_ids,
affix_bos=False,
affix_eos=False,
),
remove_columns=decoder_dataset.column_names,
)
training_dataset = encoder_dataset.map(
lambda example, idx: get_relational_input_ids(
example,
idx,
vocab,
in_df.columns,
decoder_dataset,
in_out_idx,
output_max_length,
),
remove_columns=encoder_dataset.column_names,
with_indices=True,
)
# If the output_max_length variable is specified, filter
# observations that exceed this length. The
# `get_relational_input_ids` should have set the
# `labels` to None if the output exceeds `output_max_length`.
if output_max_length:
init_data_length = training_dataset.shape[0]
training_dataset = training_dataset.filter(
lambda example: example["labels"] is not None
)
removed_count = init_data_length - training_dataset.shape[0]
if removed_count > 0:
warnings.warn(
f"A total of {removed_count} out of {init_data_length} has been removed from the training data because they exceeded the `output_max_length` of {output_max_length}."
)
return training_dataset